Operational IT Model
Operational IT Model
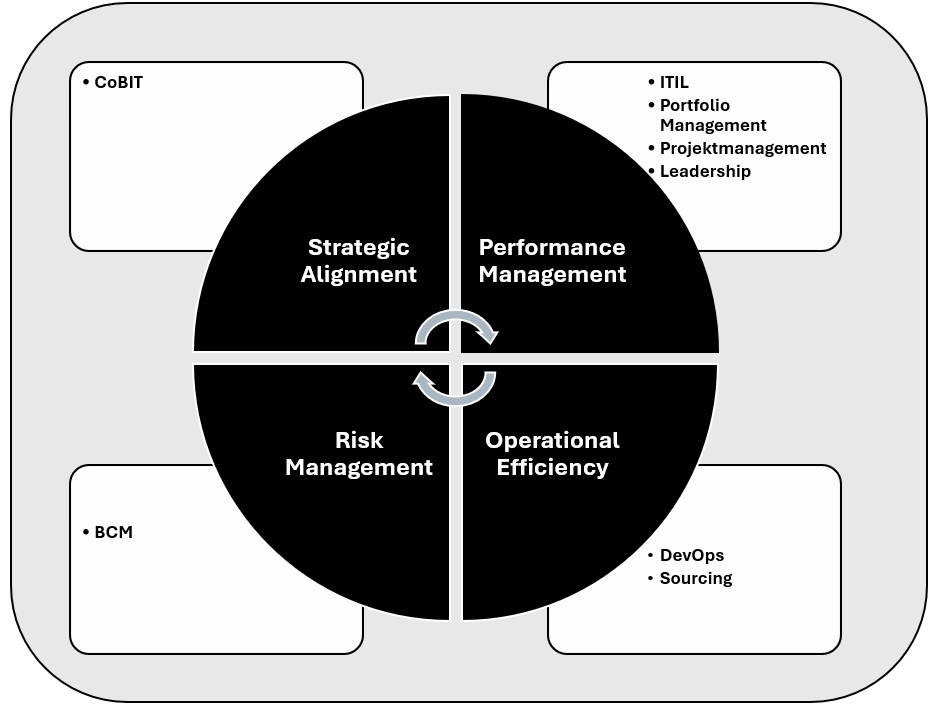
The operational IT Model is derived from the corporate strategy. It is based on the pillars of Strategic Alignment, Performance Management, Operational Efficiency, and Risk Management. This consulting is complemented by established frameworks such as COBIT and ITIL.
The operational (IT) model is largely determined by IT Governance and IT Compliance.
IT Governance and IT Compliance are closely linked and each contributes to a company being efficient and ethical.
Where IT governance supports business objectives and minimizes risks, compliance refers to adhering to legal regulations, industry standards, and internal guidelines.

The operational IT Model is derived from the corporate strategy. It is based on the pillars of Strategic Alignment, Performance Management, Operational Efficiency, and Risk Management. This consulting is complemented by established frameworks such as COBIT and ITIL.
The operational (IT) model is largely determined by IT Governance and IT Compliance.
IT Governance and IT Compliance are closely linked and each contributes to a company being efficient and ethical.
Where IT governance supports business objectives and minimizes risks, compliance refers to adhering to legal regulations, industry standards, and internal guidelines.
Strategic Alignment
IT Governance – what is it? There's no single, universally accepted definition.
We call it "management of (IT) management."
It's about the responsibility of top management for a smoothly functioning IT environment that supports business models.
COBIT 2019 enables holistic governance and management. The framework was published by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association). ISACA is an independent, global professional association for IT auditors, accountants, and experts in information security and IT governance.
COBIT uses a three-dimensional approach in its analysis. Across four domains, processes and activities in the context of resources – applications, information, infrastructure, and people – are analyzed and monitored with regard to seven KPIs (effectiveness, efficiency, confidentiality, integrity, compliance, and reliability). This provides top management with up-to-date transparency regarding the company's IT status at all times.
External consulting supports the implementation of the COBIT framework, the structured recording and documentation of the individual topics, and the creation of transparency regarding IT Governance.
Performance Management
The areas of IT controlling and IT Sourcing are particularly important for operational efficiency.
IT controlling provides necessary management information for decision-making based on data from the company's own IT operations – often in relation to standard market values.
IT Sourcing is the procurement strategy for processes and functions as an aspect of an IT operating model. In a broader sense, a distinction is made between keeping processes and functions within the company, insourcing (bringing them back in), and outsourcing (outsourcing) processes and functions. External consulting supports the transformation of KPIs and metrics into information that serves as an essential basis for decision-making for top management.
Furthermore, it provides the criteria that are of crucial importance as a basis for consideration in the decision-making process for “IT sourcing”.
Operational Efficiency
ITIL deals with all possibilities of value creation between Service Provider (IT) and Service Consumer (user).
The framework addresses goals for the continuous improvement of services and defines activities to improve service quality as well as processes with clear goals and metrics.
The ITIL principle applies: If you can't measure it, you can't control it.
As part of the strategy development process, IT services are defined, developed, and incorporated into the service portfolio, both initially and in regular cycles. Based on this, ITIL artifacts such as incident, service, and change management are defined and integrated into IT processes.
Risk Management
IT Risk Management is the process of analyzing threats to a company's IT infrastructure and assessing the level of risk a company is willing to accept. The goal of IT risk management is to protect the company's IT systems and data from potential damage and threats, thereby ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of the company's IT infrastructure and data.
Here, the Business Continuity Management framework is used to implement all preventative measures regarding IT security and data protection within a company. Business continuity encompasses the ability to maintain business operations within an organization even under emergency conditions.
Business Continuity Management (BCM) includes the development of strategies, concrete actions and plans, as well as an organizational structure for emergency response. It protects organizations from operational disruptions and demonstrates alternative procedures under emergency conditions.
Strategic Alignment
IT Governance – what is it? There's no single, universally accepted definition.
We call it "management of (IT) management."
It's about the responsibility of top management for a smoothly functioning IT environment that supports business models.
COBIT 2019 enables holistic governance and management. The framework was published by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association). ISACA is an independent, global professional association for IT auditors, accountants, and experts in information security and IT governance.
COBIT uses a three-dimensional approach in its analysis. Across four domains, processes and activities in the context of resources – applications, information, infrastructure, and people – are analyzed and monitored with regard to seven KPIs (effectiveness, efficiency, confidentiality, integrity, compliance, and reliability). This provides top management with up-to-date transparency regarding the company's IT status at all times.
External consulting supports the implementation of the COBIT framework, the structured recording and documentation of the individual topics, and the creation of transparency regarding IT Governance.
Performance Management
The areas of IT controlling and IT Sourcing are particularly important for operational efficiency.
IT controlling provides necessary management information for decision-making based on data from the company's own IT operations – often in relation to standard market values.
IT Sourcing is the procurement strategy for processes and functions as an aspect of an IT operating model. In a broader sense, a distinction is made between keeping processes and functions within the company, insourcing (bringing them back in), and outsourcing (outsourcing) processes and functions. External consulting supports the transformation of KPIs and metrics into information that serves as an essential basis for decision-making for top management.
Furthermore, it provides the criteria that are of crucial importance as a basis for consideration in the decision-making process for “IT sourcing”.
Operational Efficiency
ITIL deals with all possibilities of value creation between Service Provider (IT) and Service Consumer (user).
The framework addresses goals for the continuous improvement of services and defines activities to improve service quality as well as processes with clear goals and metrics.
The ITIL principle applies: If you can't measure it, you can't control it.
As part of the strategy development process, IT services are defined, developed, and incorporated into the service portfolio, both initially and in regular cycles. Based on this, ITIL artifacts such as incident, service, and change management are defined and integrated into IT processes.
Risk Management
IT Risk Management is the process of analyzing threats to a company's IT infrastructure and assessing the level of risk a company is willing to accept. The goal of IT risk management is to protect the company's IT systems and data from potential damage and threats, thereby ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of the company's IT infrastructure and data.
Here, the Business Continuity Management framework is used to implement all preventative measures regarding IT security and data protection within a company. Business continuity encompasses the ability to maintain business operations within an organization even under emergency conditions.
Business Continuity Management (BCM) includes the development of strategies, concrete actions and plans, as well as an organizational structure for emergency response. It protects organizations from operational disruptions and demonstrates alternative procedures under emergency conditions.
